Hodgkin Lymphoma Causes Unrelated to AFFF Exposure
We've identified several causes of Hodgkin Lymphoma unrelated to AFFF exposure, including genetic predisposition, immune system vulnerabilities, and Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) infection. A family history of lymphatic cancers or autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, markedly raises the risk. Environmental factors, like exposure to benzene and pesticides, also play an essential role. Additionally, lifestyle choices and socioeconomic status can affect one's susceptibility to this type of cancer. By understanding these varied causes, we can develop more effective prevention and treatment strategies. A deeper exploration will expand on the complexity of these factors.
Key Takeaways
- Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) infection triggers genetic changes in lymphocytes, significantly increasing Hodgkin lymphoma risk.
- Genetic predisposition, including family history of lymphatic cancers, enhances susceptibility to Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Exposure to chemicals like benzene and pesticides in the environment raises the risk of developing Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, compromise the immune system and elevate cancer susceptibility.
- Lifestyle factors, including smoking, excessive alcohol use, and obesity, are significant risk factors for Hodgkin lymphoma.
Genetic Predisposition
We've discovered that a genetic predisposition greatly influences the risk of developing Hodgkin lymphoma, beyond any environmental exposures. This implies that even without encountering known carcinogens, individuals with certain genetic backgrounds may still face a higher risk. It is crucial to comprehend that specific genetic mutations and changes can greatly enhance one's susceptibility to Hodgkin lymphoma. These genetic factors are complex and varied, suggesting that the risk is not uniform across all populations.
Moreover, a family history of Hodgkin lymphoma or other lymphatic cancers can often act as a clear indicator of a genetic predisposition to the disease. It is not unusual for individuals with close relatives who have fought Hodgkin lymphoma to find themselves at a greater risk. This familial pattern underscores the importance of genetic factors in evaluating one's risk.
Certain genetic syndromes have also been associated with an increased risk of developing Hodgkin lymphoma. Familial Hodgkin lymphoma, for example, represents a more direct connection between genetics and the disease, pointing to heritable factors that predispose individuals to Hodgkin lymphoma.
Understanding these genetic factors is critical for both personalized treatment and risk evaluation. By recognizing the role of genetic predisposition, healthcare providers can tailor their approaches to each individual's unique genetic makeup, offering more targeted and effective interventions. This knowledge not only aids in the early detection and treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma but also in the development of strategies to manage and possibly mitigate the risk for those identified as genetically predisposed.
Immune System Vulnerabilities
Having explored the genetic predispositions, it's now important to examine how immune system vulnerabilities play a significant role in the development of Hodgkin lymphoma. It's well understood that factors weakening the immune system, whether due to genetic reasons or immunodeficiency disorders, considerably heighten the risk of encountering this disease. We're aware that certain infections can impact the immune system, yet it's essential to concentrate on how inherent immune system vulnerabilities contribute independently to Hodgkin lymphoma, steering clear of specific infection discussions.
Autoimmune diseases or chronic inflammatory conditions are notable for maintaining a state of prolonged immune system activation. This sustained activity doesn't just wear down the body's defenses but also paves the way for Hodgkin lymphoma by creating an environment ripe for such malignancies. Additionally, a family history of Hodgkin lymphoma or other lymphoid malignancies underscores a potential genetic component, suggesting that specific inherited immune system vulnerabilities could increase susceptibility to the disease.
Moreover, exposure to environmental factors, including radiation or certain chemicals not related to AFFF, can adversely affect the immune system. Such exposures might not directly cause Hodgkin lymphoma, but they weaken the immune defenses, making the body more susceptible to diseases that could trigger the lymphoma.
In essence, understanding the multifaceted roles of immune system vulnerabilities in Hodgkin lymphoma development is crucial. It's not just about the direct triggers but also about how an individual's immune system can make them more susceptible to this complex disease.
Epstein-Barr Virus Infection
We've come to understand that the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) plays a significant role in the development of Hodgkin lymphoma, especially concerning how it interacts with our immune systems. This connection has led researchers to explore the mechanisms through which EBV infection may prompt the onset of lymphoma, focusing on its ability to cause B-cell proliferation. By examining the presence of EBV in tumors, it's evident there's an important link to the disease's initiation and progression.
Link to Lymphoma Development
Exploring the connection between Epstein-Barr virus infection and Hodgkin lymphoma reveals how this virus acts as a significant risk factor for the disease. We've understood that Epstein-Barr virus infection is a known risk factor, leading to genetic changes in lymphocytes which heighten the risk of developing lymphoma. Remarkably, this virus is linked to approximately 30-40% of Hodgkin lymphoma cases in developed countries. The infection's ability to trigger abnormal immune responses further contributes to the development of this type of lymphoma. It's essential for us to grasp the association between Epstein-Barr virus and Hodgkin lymphoma, as it is vital for devising targeted prevention and treatment strategies, ultimately mitigating the risk factors involved.
Infection Mechanisms Explored
To understand how the Epstein-Barr virus contributes to Hodgkin lymphoma, it's important to explore the mechanisms of infection it employs. EBV infection is a common occurrence worldwide, but it doesn't always lead to serious health issues. However, in those with compromised immune systems, the story changes dramatically. Here, EBV can trigger the onset of lymphomas, including Hodgkin lymphoma. This is because the virus can induce genetic mutations and immune responses that are conducive to the development of this cancer. Additionally, research has shown that Hodgkin lymphoma linked to EBV infection often presents with unique clinical and biological characteristics compared to cases where EBV is not involved. Understanding these mechanisms is essential in developing targeted therapies and prevention strategies.
Chemical Exposure Risks
Exposure to certain chemicals, including benzene and pesticides, greatly enhances the risk of developing Hodgkin lymphoma. When we explore further into the chemical exposure risks, it's evident that our everyday environments may harbor agents that could potentially contribute to this condition. Research highlights that not only are industrial workers at risk, but also individuals who frequently come into contact with household chemicals found in hair dyes, paints, and cleaning products.
Occupational exposure is particularly concerning, with substances like formaldehyde, asbestos, and solvents being linked to an increased risk of Hodgkin lymphoma. These chemicals are often encountered in various industries, including manufacturing and agriculture, where herbicides and fungicides are regularly used. It's also important to note that individuals exposed to chemicals used in agriculture or those working with industrial chemicals, such as vinyl chloride and benzidine, may face a higher risk.
Understanding these risks is vital for both individuals and healthcare professionals. It underscores the importance of protective measures and regulations to minimize exposure to these harmful chemicals. Moreover, this knowledge empowers us to advocate for safer practices in both our professional and personal lives.
As we navigate through the complexities of Hodgkin lymphoma causes, it's clear that chemical exposure plays a significant role. However, it's important to remember that this is just one piece of the puzzle. By continuing to investigate and address these risks, we can work towards reducing the incidence of Hodgkin lymphoma and ensuring a healthier environment for all.
Autoimmune Diseases Connection
Moving beyond chemical exposure, we're now turning our attention to the connection between autoimmune diseases and Hodgkin lymphoma. It's become evident that conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus might not only compromise one's immune system but also elevate the risk of this type of cancer. As we investigate this correlation, it's vital for individuals with autoimmune conditions to stay vigilant through regular health screenings.
Autoimmune Triggers Explored
Several autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, have been identified as potential triggers for Hodgkin lymphoma, highlighting the intricate link between autoimmune dysfunction and the development of this type of cancer. We've found that these autoimmune triggers play a significant role independently of AFFF exposure. It's important to understand that specific autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus not only contribute to the risk of developing Hodgkin lymphoma but also spotlight the broader issue of immune system dysfunction in these diseases. This dysfunction can lead to lymphoma development. Additionally, a blend of genetic predisposition and environmental factors underlines the complexity of autoimmune-related Hodgkin lymphoma. Grasping the significance of these autoimmune triggers is essential in diagnosing and treating cases unrelated to AFFF exposure.
Immune Response Link
Delving into the connection between autoimmune diseases and Hodgkin lymphoma, it's apparent that an abnormal immune response may serve as a vital trigger for the cancer's development. Autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus can initiate a chronic inflammation process, independently contributing to Hodgkin lymphoma, separate from any AFFF exposure. This underscores the importance of understanding the immune response link in the disease's onset. Genetic predispositions, alongside environmental factors, play a significant role in this correlation, emphasizing the complexity of the immune system's dysregulation in autoimmune diseases. It's essential for us to grasp this intricate relationship to enhance diagnosis and treatment strategies, recognizing that the immune response link is a pivotal factor in lymphoma risk.
Age-Related Factors
As we age, our risk of developing Hodgkin lymphoma increases, particularly in two key age groups: young adults aged 15-40 and those over 55. This fact underscores the significant role that age-related factors play in the onset of this type of cancer. It's evident that as individuals grow older, the likelihood of encountering Hodgkin lymphoma rises, with a notable peak in risk for those who are over the age of 55. This pattern reveals a critical insight into the disease's epidemiology, showing a distinct age-related vulnerability.
It's important to note that while Hodgkin lymphoma is relatively rare in children under the age of 5, the risk begins to gradually increase with age. This uptick in risk is not uniform across all age groups but is particularly pronounced in young adults and then again in older adults, after the age of 55. The reasons behind this pattern are multifaceted, encompassing age-related changes in the immune system and the accumulation of genetic mutations over time. These factors contribute to the increased susceptibility to Hodgkin lymphoma as people age.
Understanding these age-related factors is vital for identifying at-risk populations and for guiding future research and prevention strategies. It's also instrumental in informing the public about the importance of being vigilant for the signs and symptoms of Hodgkin lymphoma, especially as they age. By acknowledging the significant role that age plays in the development of Hodgkin lymphoma, we can better prepare and protect those most at risk.
Gender Influence
While gender doesn't directly cause Hodgkin lymphoma, the slight disparity in incidence rates between males and females invites further exploration. We've observed that the incidence of Hodgkin lymphoma is marginally higher in males than in females, with a ratio of around 1.3:1. This subtle difference underscores the necessity to investigate the gender influence on this disease, shedding light on how hormonal factors related to gender might play a role, albeit the exact mechanisms remain elusive.
We understand that both genders are susceptible to Hodgkin lymphoma, emphasizing that gender does not substantially influence the development of this condition. However, the nuances in how gender impacts the age of onset and the specific symptoms experienced by individuals cannot be overlooked. It's important to acknowledge these variations, as they offer insights into the disease's behavior and possibly its management.
Moreover, the treatment approaches and outcomes for Hodgkin lymphoma generally show no significant difference between males and females. This observation suggests that, despite the slight gender influence on incidence rates, the effectiveness of treatment remains consistent across genders. It's a reassurance that the medical community's efforts to combat Hodgkin lymphoma consider the slight gender-based variations without allowing them to dictate the course of treatment.
Family History Significance
Family history greatly influences an individual's risk of developing Hodgkin lymphoma, underscoring the need for thorough genetic evaluations in at-risk populations. When we investigate the dynamics of Hodgkin lymphoma, we find that a person's family history is a pivotal factor. If a close family member has battled this disease, the risk escalates, highlighting the importance of understanding one's genetic background.
Inherited genetic mutations, often passed down through generations, can markedly heighten an individual's susceptibility to Hodgkin lymphoma. These genetic predispositions mean that some individuals are inherently more prone to developing this condition, irrespective of exposure to environmental factors such as Aqueous Film Forming Foam (AFFF). It's essential to recognize that these genetic factors are a core component of the risk landscape for Hodgkin lymphoma, independent of any external exposures.
The role of family history in Hodgkin lymphoma isn't just about identifying risk. It's about utilizing this knowledge for early detection and crafting tailored treatment plans that accommodate the unique genetic makeup of at-risk individuals. A thorough evaluation of family history is, hence, central to managing and mitigating the risk of Hodgkin lymphoma. It allows for a proactive approach in monitoring and potentially preventing the onset of this disease among those with a significant family history.
Socioeconomic Status

We've noticed that lower socioeconomic status often correlates with an increased risk of developing Hodgkin lymphoma. Studies have emphasized this connection, suggesting that factors such as limited access to healthcare and poorer living conditions play a noteworthy role in this inequality. It's evident that socioeconomic status, covering elements like education level and income, can markedly impact an individual's likelihood of facing this type of cancer.
Furthermore, those from disadvantaged socioeconomic backgrounds encounter additional obstacles in obtaining a timely diagnosis and treatment for Hodgkin lymphoma. This delay can worsen the condition, leading to poorer outcomes compared to individuals with better access to healthcare services. Recognizing the influence of socioeconomic status on the incidence and management of Hodgkin lymphoma is vital. It highlights the need for targeted interventions to bridge these gaps and ensure equitable healthcare access for all, regardless of their economic or social standing.
Addressing these disparities requires a multifaceted approach. Efforts should focus on improving healthcare accessibility, enhancing education around the importance of early diagnosis, and potentially tailoring treatment plans to accommodate the unique challenges faced by individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds. By acknowledging and acting upon the link between socioeconomic status and Hodgkin lymphoma risk, we can make strides towards reducing healthcare inequalities and improving outcomes for all affected by this condition.
Lifestyle Contributions
Turning our attention to lifestyle contributions, we find that certain habits notably impact the risk of developing Hodgkin lymphoma. Smoking and excessive alcohol use, coupled with obesity and a poor diet, have emerged as notable factors in the onset of this disease. It's essential for us to understand how these lifestyle choices, alongside physical inactivity, contribute to the overall risk profile for Hodgkin lymphoma.
Smoking and Alcohol Use
Exploring the impact of lifestyle choices, it's evident that smoking and excessive alcohol consumption substantially raise the risk of Hodgkin lymphoma. Smokers, in particular, face a higher likelihood of developing this disease compared to non-smokers. The evidence is clear: tobacco smoke exposure is directly linked to an increased incidence of Hodgkin lymphoma. Additionally, alcohol consumption, especially among heavy or chronic drinkers, is associated with a heightened risk. When these two factors combine—smoking and heavy alcohol use—the risk of developing Hodgkin lymphoma escalates even further. It's important to understand that these lifestyle choices, namely smoking and excessive alcohol intake, can independently contribute to the onset of Hodgkin lymphoma, setting aside any potential exposure to AFFF.
Obesity and Diet Impact
Delving into lifestyle contributions, it's clear that obesity and dietary habits play important roles in the risk of developing Hodgkin lymphoma. We've identified obesity as a significant risk factor, independent of AFFF exposure. Poor dietary choices, especially those high in processed foods and low in fruits and vegetables, may also contribute to the development of this condition. Research points towards obesity-related inflammation as a potential link to an increased risk. We're learning that maintaining a healthy weight and adopting a balanced diet could help in reducing this risk. Additionally, lifestyle factors such as physical inactivity and unhealthy eating patterns can weaken the body's immune system, potentially heightening susceptibility to Hodgkin lymphoma. It's essential we recognize these lifestyle contributions to better understand and mitigate the risks associated with Hodgkin lymphoma.
Geographic Variations
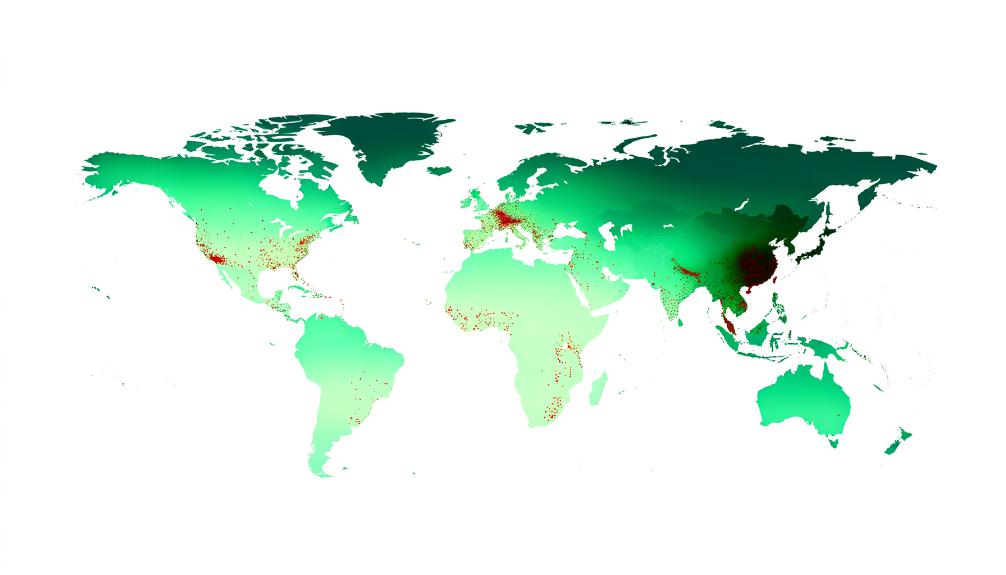
Hodgkin lymphoma's incidence varies globally, with developed countries reporting higher rates. It's evident that regions boasting higher socioeconomic status and better healthcare access witness an uptick in Hodgkin lymphoma cases. This observation hints at a complex interplay of factors at work, beyond what's immediately apparent.
Delving into this disparity, it becomes clear that environmental factors play a significant role. Urbanization and pollution, prevalent in more developed areas, may contribute to the geographic differences in Hodgkin lymphoma rates observed. It's not just about the air we breathe or the water we drink; it's about how these environmental conditions interact with our bodies on a cellular level.
Moreover, variances in viral exposure and genetic predispositions across different regions can impact the occurrence of Hodgkin lymphoma. These elements suggest a deeply woven narrative where environment, lifestyle, and genetics converge to influence risk. Studies underline this point, suggesting that environmental factors, alongside lifestyle choices and genetic factors, interact to shape Hodgkin lymphoma risk globally.
We're faced with a multifaceted issue where addressing one factor won't suffice. It's about understanding the broader context—how these elements interplay and what it means for regions with differing levels of development and environmental exposure. The geographic variations in Hodgkin lymphoma incidence highlight a need for targeted research and tailored health strategies that address the unique challenges and risk factors present in each region.
Previous Cancer Treatments
We're now turning our attention to how previous cancer treatments, specifically chemotherapy and radiation therapy, can substantially raise the risk of developing Hodgkin lymphoma. It's important to understand that individuals who have undergone radiation therapy, especially targeting the chest area, are at a heightened risk. This is due to the direct exposure of lymphatic tissues to radiation, which can trigger mutations leading to Hodgkin lymphoma.
Moreover, chemotherapy drugs, including alkylating agents and topoisomerase II inhibitors, have been identified as potential culprits in causing secondary Hodgkin lymphoma. These agents are known for their ability to interfere with DNA, which, while effective in killing cancer cells, may also inadvertently harm healthy cells and increase the likelihood of developing another form of cancer.
For those with a history of cancer treatments, it's important to be aware of this increased risk. While these treatments are often necessary and life-saving, they do come with long-term implications that need to be monitored. This heightened risk underscores the importance of regular follow-up care and surveillance for individuals who have received cancer treatments in the past.
Understanding the impact of past cancer treatments on the risk of Hodgkin lymphoma is crucial. It helps in early detection and intervention, improving the outcome for those affected. It's also a reminder of the delicate balance required in cancer treatment—targeting the disease while minimizing the risk of future health issues. As we continue to explore the causes of Hodgkin lymphoma unrelated to AFFF exposure, the role of previous cancer treatments remains a critical area of focus.

This post has been generated by AI and was not reviewed by editors. This is Not legal advice. Please consult with an attorney.



